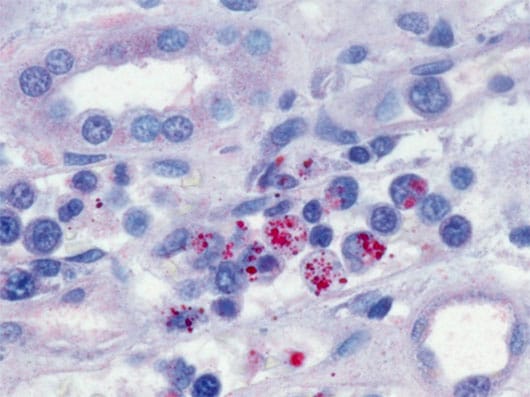
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Functional Characterization of Multiple Ehrlichia chaffeensis Sodium (Cation)/Proton Antiporter Genes Involved in the Bacterial pH Homeostasis

Ehrlichia Isolate from a Minnesota Tick: Characterization and Genetic Transformation | Applied and Environmental Microbiology

Molecular and cellular pathobiology of Ehrlichia infection: targets for new therapeutics and immunomodulation strategies | Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine | Cambridge Core
Ehrlichia chaffeensis TRP120-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of tumor suppressor FBW7 increases oncoprotein stability and promotes infection | PLOS Pathogens
Ehrlichia chaffeensis Uses Its Surface Protein EtpE to Bind GPI-Anchored Protein DNase X and Trigger Entry into Mammalian Cells | PLOS Pathogens
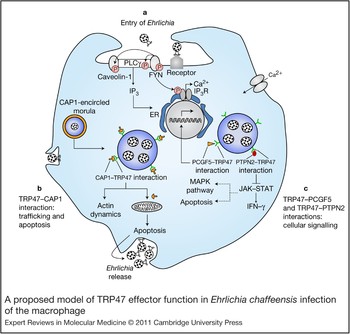
Molecular and cellular pathobiology of Ehrlichia infection: targets for new therapeutics and immunomodulation strategies | Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine | Cambridge Core
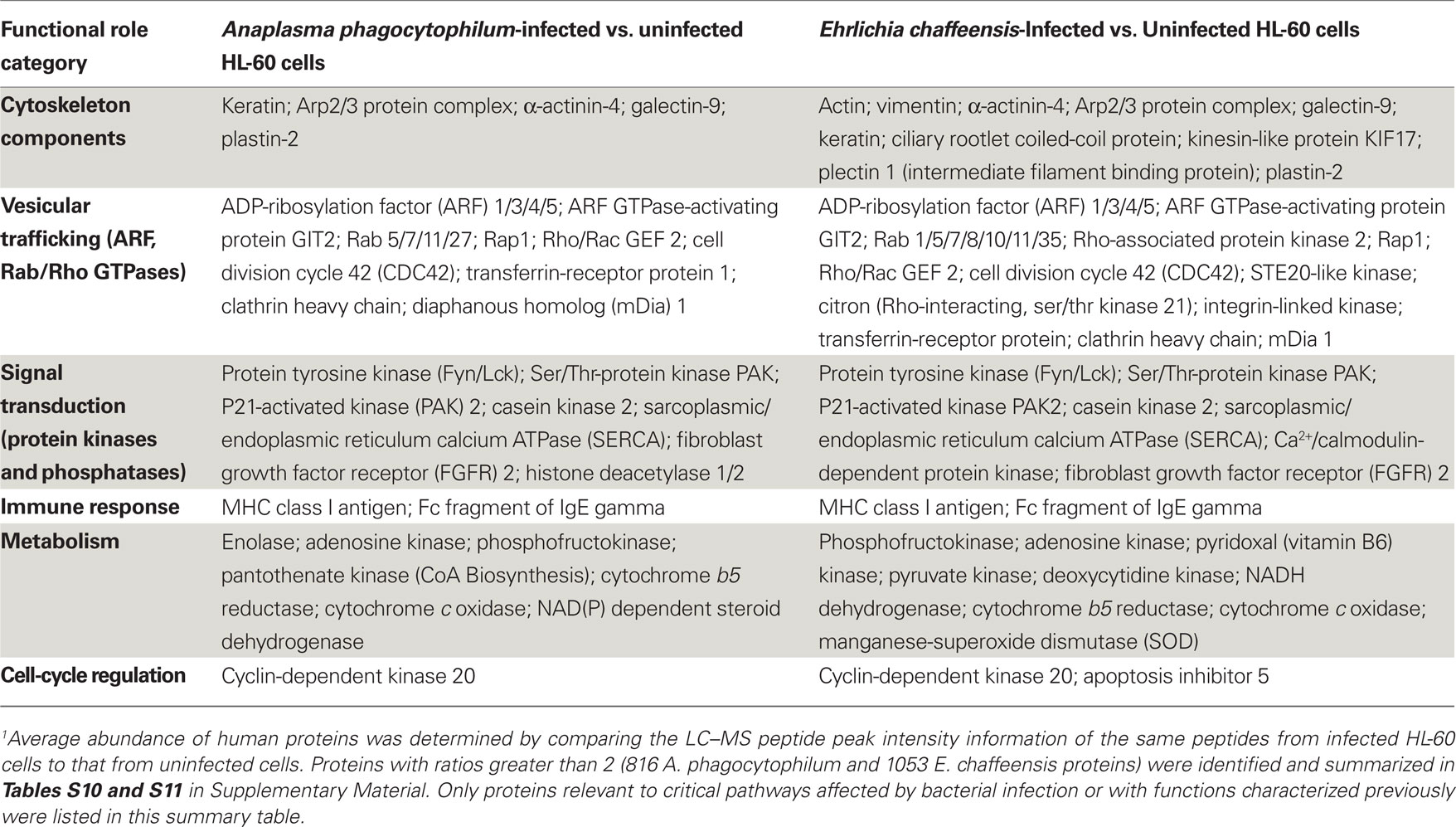
Frontiers | Global Proteomic Analysis of Two Tick-Borne Emerging Zoonotic Agents: Anaplasma Phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia Chaffeensis
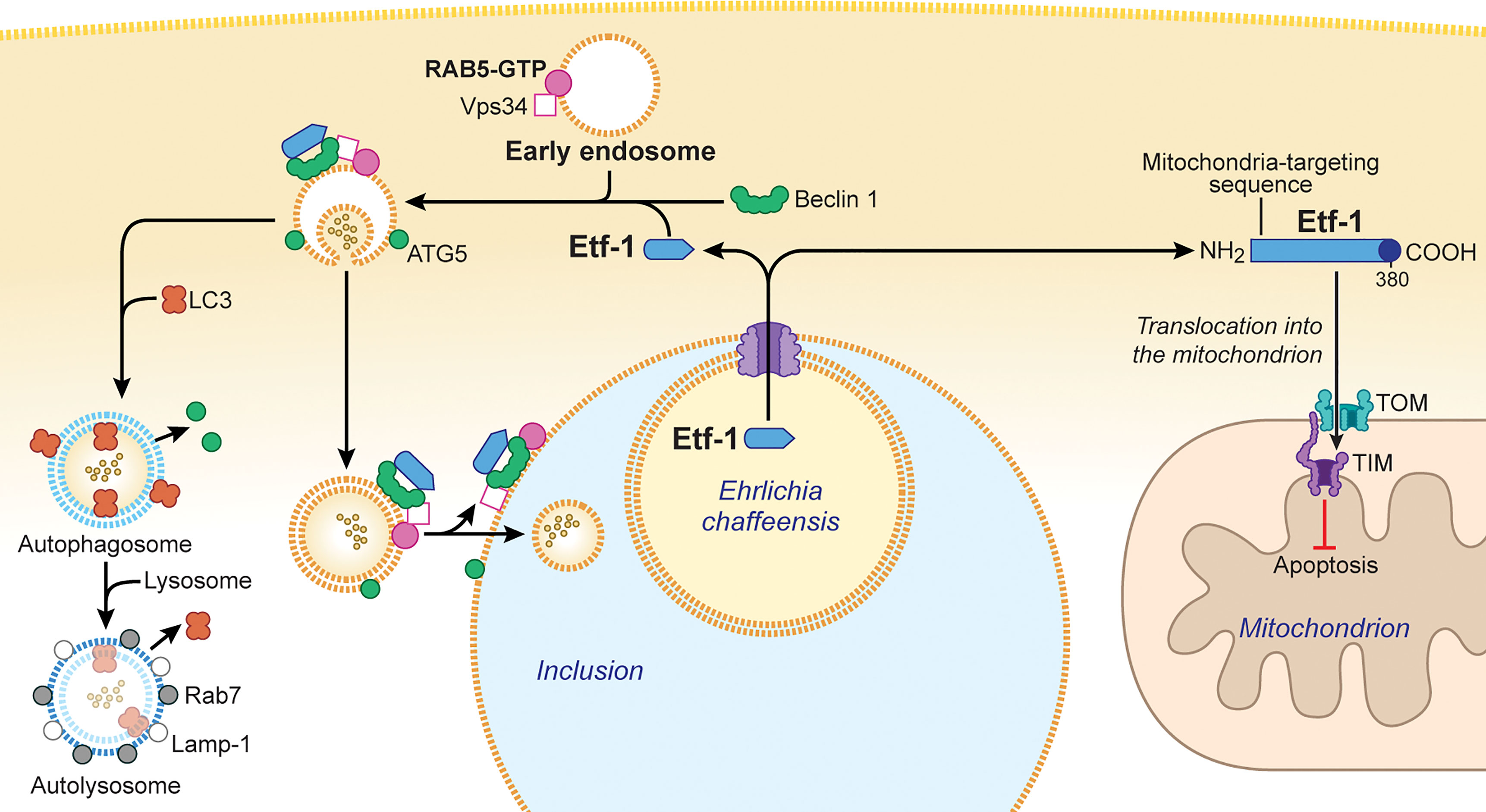
Frontiers | The “Biological Weapons” of Ehrlichia chaffeensis: Novel Molecules and Mechanisms to Subjugate Host Cells

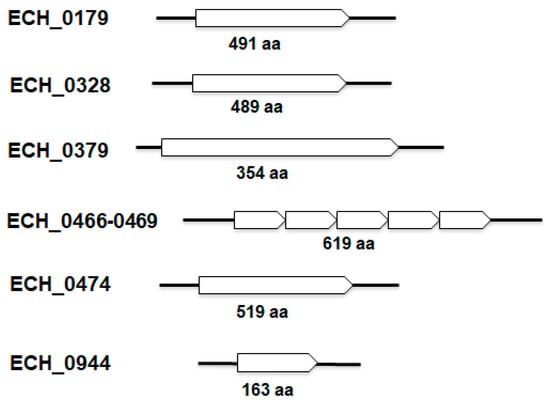
Comparative Analysis of Genome of Ehrlichia sp. HF, a Model Bacterium to Study Fatal Human Ehrlichiosis | BMC Genomics | Full Text
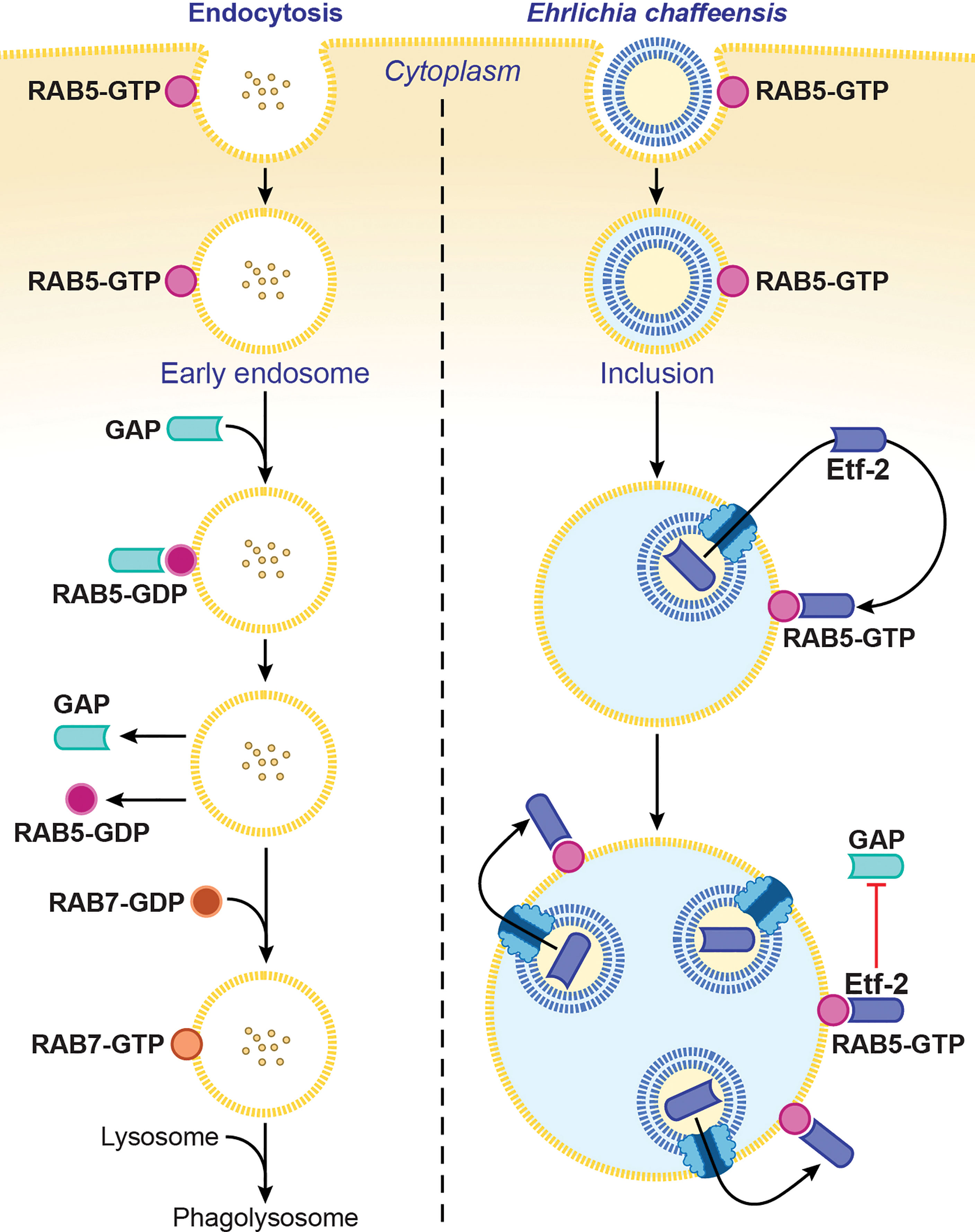
Frontiers | The “Biological Weapons” of Ehrlichia chaffeensis: Novel Molecules and Mechanisms to Subjugate Host Cells
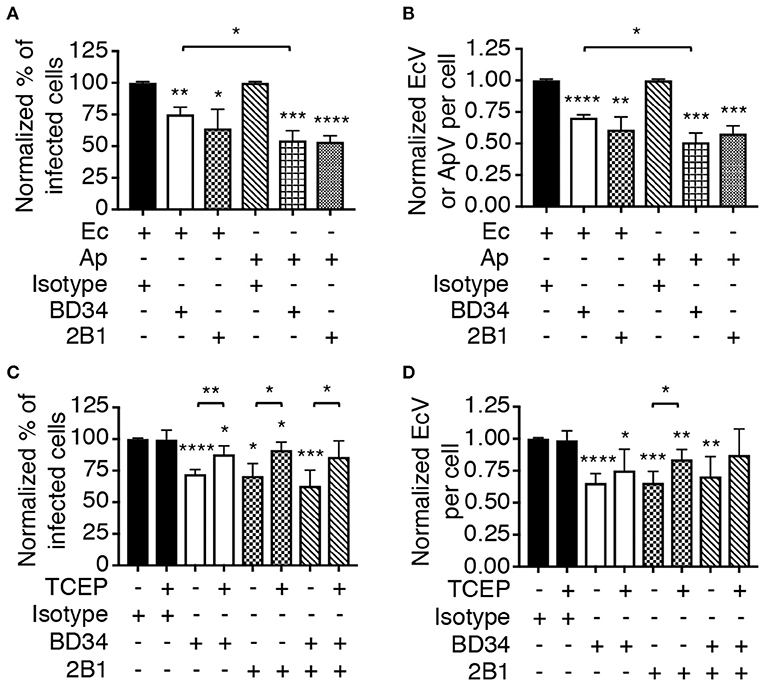
Frontiers | Ehrlichia chaffeensis EplA Interaction With Host Cell Protein Disulfide Isomerase Promotes Infection

Molecular events involved in cellular invasion by Ehrlichia chaffeensis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum - ScienceDirect
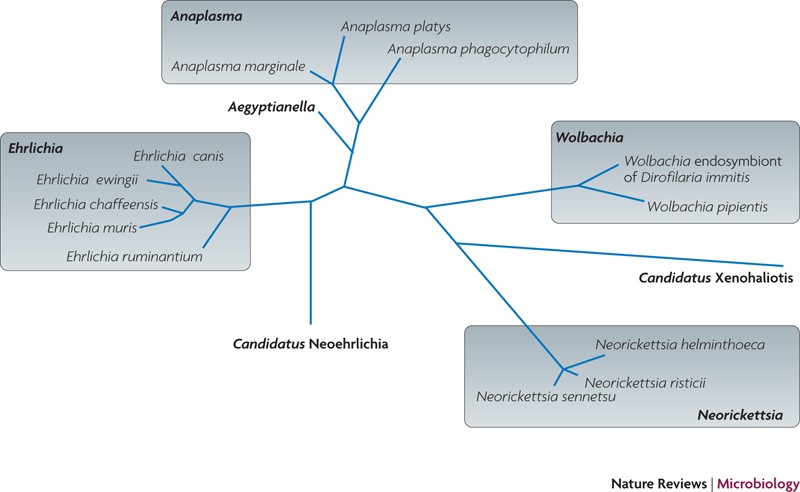
Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia chaffeensis: subversive manipulators of host cells | Nature Reviews Microbiology
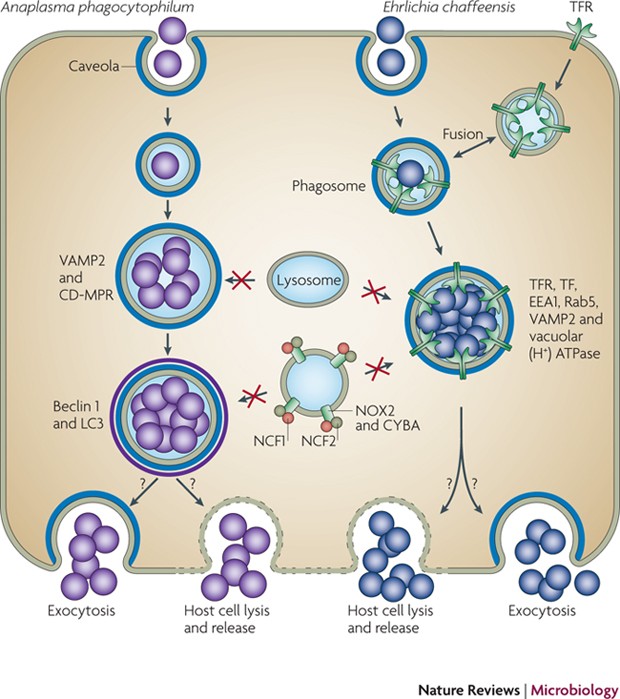
Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia chaffeensis: subversive manipulators of host cells | Nature Reviews Microbiology
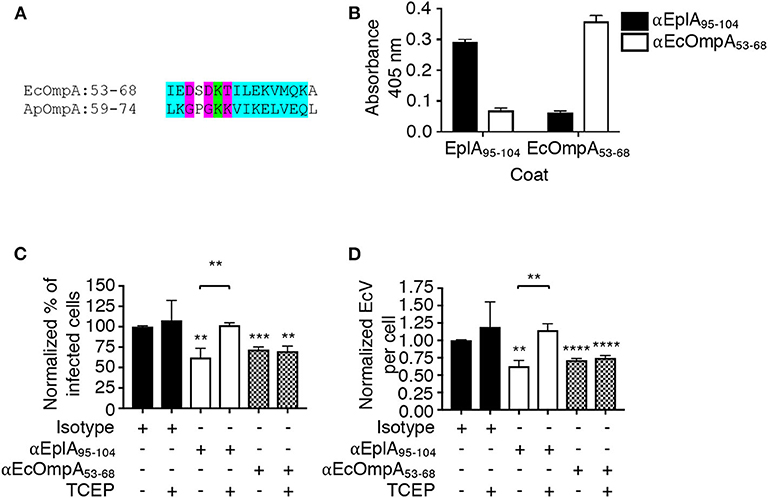
Frontiers | Ehrlichia chaffeensis EplA Interaction With Host Cell Protein Disulfide Isomerase Promotes Infection
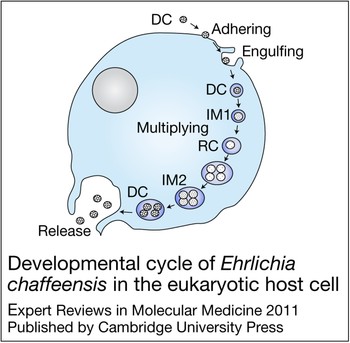
Molecular and cellular pathobiology of Ehrlichia infection: targets for new therapeutics and immunomodulation strategies | Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine | Cambridge Core
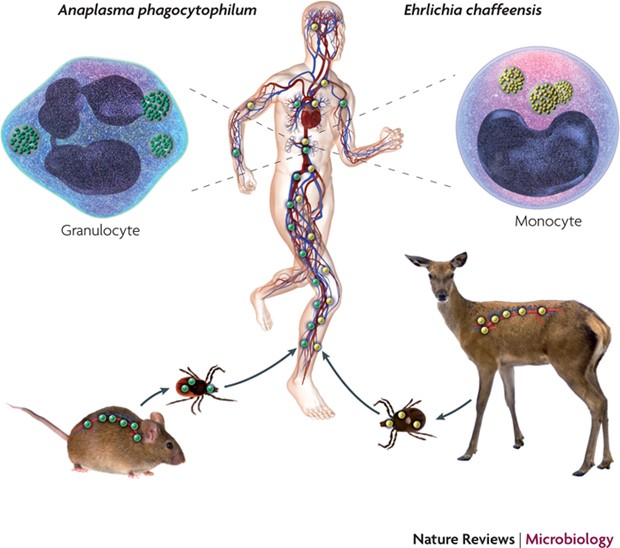
Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia chaffeensis: subversive manipulators of host cells | Nature Reviews Microbiology
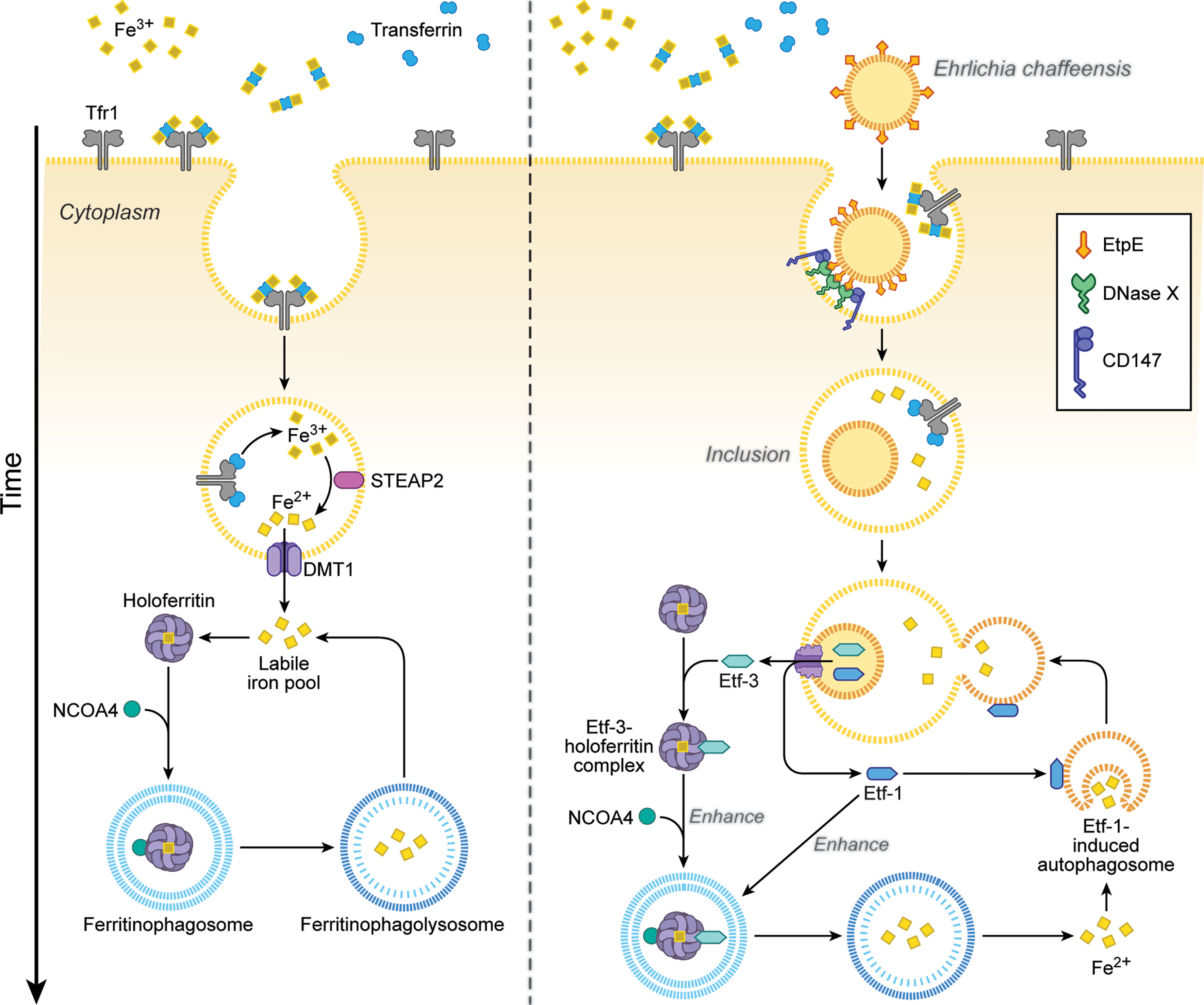
Frontiers | The “Biological Weapons” of Ehrlichia chaffeensis: Novel Molecules and Mechanisms to Subjugate Host Cells